单元测试案例
在日常的springboot项目开发中,总会需要写一些单元测试用例,一些单元测试的方法用的比较少,编写时又需要去查询,因此在此总结一些测试案例
Junit是目前主流的单元测试框架,我,常用的为Junit4,以下测试案例是基于Junit4来编写
代码地址:https://github.com/x104859/test-case
单元测试的目的与好处
1. 单元测试能有效地帮你发现代码中的 bug
单元测试往往需要走通方法中的各条路径,通过单元测试常常会发现代码中的很多考虑不全面的地方
2、写单元测试能帮你发现代码设计上的问题
对于一段代码,如果很难为其编写单元测试,或者单元测试写起来很吃力,需要依靠单元测试框架里很高级的特性才能完成,那往往就意味着代码设计得不够合理
3、单元测试是对集成测试的有力补充
对于一些复杂系统来说,集成测试也无法覆盖得很全面。复杂系统往往有很多模块。每个模块都有各种输入、输出、异常情况,组合起来,整个系统就有无数测试场景需要模拟,无数的测试用例需要设计,再强大的测试团队也无法穷举完备
4、写单元测试的过程本身就是代码重构的过程
设计和实现代码的时候,我们很难把所有的问题都想清楚。而编写单元测试就相当于对代码的一次自我 Code Review,在这个过程中,我们可以发现一些设计上的问题(比如代码设计的不可测试)以及代码编写方面的问题(比如一些边界条件处理不当)等,然后针对性的进行重构。
所需依赖
<!-- 使用MockMvc发起请求时需要该依赖, Spring Boot 2.2.0版本开始引入 JUnit5 作为单元测试默认库 JUnit5和JUnit4之间会有冲突,这里屏蔽掉JUnit5--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId> </exclusion> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId> </exclusion> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- junit4所需测试依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- 使用powermock所需依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.powermock</groupId> <artifactId>powermock-module-junit4</artifactId> <version>2.0.9</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.powermock</groupId> <artifactId>powermock-api-mockito2</artifactId> <version>2.0.9</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mockito</groupId> <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId> <version>3.12.4</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
常见注解
@Before:初始化方法,在任何一个测试方法执行之前,必须执行的代码
@BeforeClass:针对所有测试,也就是整个测试类中,在所有测试方法执行前,都会先执行由它注解的方法,而且只执行一次,修饰符必须是 public static void
@After:释放资源,在任何一个测试方法执行之后,需要进行的收尾工作
@AfterClass:针对所有测试,也就是整个测试类中,在所有测试方法都执行完之后,才会执行由它注解的方法,而且只执行一次。修饰符必须是 public static void
@Test:测试方法,表明这是一个测试方法。在 JUnit 中将会自动被执行。对与方法的声明也有如下要求:名字可以随便取,没有任何限制,但是返回值必须为 void ,而且不能有任何参数
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class) public class AnnotationTest { public static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AnnotationTest.class); @Before public void init(){ log.info("@Before call"); } @BeforeClass public static void beforeClass(){ log.info("@BeforeClass call"); } @After public void after(){ log.info("@After call"); } @AfterClass public static void afterClass(){ log.info("@AfterClass call"); } @Test public void test01(){ log.info("test01 call"); } @Test public void test02(){ log.info("test02 call"); } }
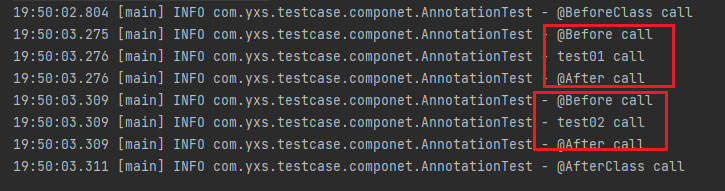
方法执行结果如下所示,两个测试方法,@Before和@After都执行了两次,而@BeforeClass和@AfterClass都只执行了一次;执行顺序:@BeforeClass --> @Before --> @Test --> @After --> @AfterClass
断言
Junit提供的断言主要有如下几种类型:
Assert.assertTrue():验证条件是否为真
Assert.assertFalse():验证条件是否为假
Assert.assertEquals():验证两个值是否相等
Assert.assertNotNull():验证对象是否为空
Assert.assertThrows():验证执行代码是否抛出了指定类型的异常
verify:
@Test
public void test(){
List list = Mockito.mock(List.class);
list.add("a");
//Mockito.times()不写默认指调用1次
Mockito.verify(list).add("a");
Mockito.verify(list,Mockito.times(1)).add("a");
//判读list.add方法被调用2次
list.add("a");
Mockito.verify(list,Mockito.times(2)).add("a");
}
@Mock与@InjectMocks的区别
@Mock: 创建一个Mock.
@InjectMocks: 创建一个实例,简单的说是这个Mock可以调用真实代码的方法,其余用@Mock注解创建的mock将被注入到用该实例中。
Mockito的初始化
当我们要使用注解(比如@Mock)来mock对象的使用,就要初始化Mockito,这样用@Mock标注的对象才会被实例化,否则直接使用会报Null指针异常。其有两种初始化的方法:
1、使用MockitoAnnotations.initMocks方法
public class InitMockA { public static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InitMockA.class); @Before public void init(){ MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); } @Test public void test01(){ log.info("run test01"); } }
2、类上使用@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class)
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class) public class InitMockB { public static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InitMockB.class); @Test public void test01(){ log.info("run test01"); } }
案例
1、常见简单测试案例
@Service public class AComponent { @Value("${test-case.key}") private String key; @Autowired private UserInfoMapper userInfoMapper; @Autowired private BComponent bComponent; public UserInfo normalMethod(Integer id){ UserInfo userInfo = userInfoMapper.getById(id); System.out.println(userInfo.getSex()); return userInfo; } public boolean compareUser(Integer originId,Integer targetId){ UserInfo originUser = userInfoMapper.getById(originId); UserInfo targetUser = userInfoMapper.getById(targetId); return originUser.getSex().equals(targetUser.getSex()); } public void complicatedService(ServiceEntity serviceEntity, String name){ //... bComponent.complicatedMethod(serviceEntity,name); //... } public UserInfo exceptionService(Integer id){ UserInfo userInfo = null; try { userInfo = bComponent.exceptionMethod(id); }catch (Exception e){ return null; } return userInfo; } public void updateUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo){ userInfoMapper.updateUserInfo(userInfo); } public String getKey(){ return key; } }
测试方法:
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class) public class SimpleTest { @Mock private UserInfoMapper userInfoMapper; @Mock private BComponent bComponent; /** * 创建一个实例,简单的说是这个Mock可以调用真实代码的方法,其余用@Mock注解创建的mock将被注入到用该实例中 */ @InjectMocks AComponent aComponent; @Before public void intit(){ // 为aComponent注入对象 ReflectionTestUtils.setField(aComponent,"key","abcdefg"); } /** * 最常见的测试用例,mock返回值 */ @Test public void normalTest(){ Integer id = 1; Mockito.when(userInfoMapper.getById(id)).thenReturn(getManUserInfo()); aComponent.normalMethod(id); Mockito.verify(userInfoMapper).getById(id); } /** * 测试同一个方法,入参不同的,返回值也不相同 */ @Test public void differentParamTest(){ Integer user1 = 1; Integer user2 = 2; Mockito.when(userInfoMapper.getById(user1)).thenReturn(getManUserInfo()); Mockito.when(userInfoMapper.getById(user2)).thenReturn(getFemaleUserInfo()); boolean result = aComponent.compareUser(user1,user2); Assert.assertFalse(result); } /** * 入参比较复杂的时候可以使用Mockito.any,入参也是可以mock的 * Mockito.any()可以有多种类型,比如: * Mockito.any(ServiceEntity.class); * Mockito.anyString(); * Mockito.anyCollection(); * Mockito.anyList(); */ @Test public void paramComplicated(){ aComponent.complicatedService(Mockito.any(),Mockito.anyString()); Mockito.verify(bComponent).complicatedMethod(Mockito.any(),Mockito.anyString()); } /** * 当方法中出现异常的时候,可以使用doThrow方法自己制造异常 */ @Test public void exceptionTest(){ Integer id = 1; Mockito.doThrow(new IllegalArgumentException()).when(bComponent).exceptionMethod(id); UserInfo userInfo = aComponent.exceptionService(id); Assert.assertTrue(userInfo == null); } @Test public void keyTest(){ String key = aComponent.getKey(); Assert.assertTrue("abcdefg".endsWith(key)); } private UserInfo getManUserInfo(){ UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo(); userInfo.setId(1); userInfo.setUserName("zhansan"); userInfo.setAge(12); userInfo.setSex("M"); return userInfo; } private UserInfo getFemaleUserInfo(){ UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo(); userInfo.setId(2); userInfo.setUserName("李四"); userInfo.setAge(12); userInfo.setSex("F"); return userInfo; } }
2、Mock静态方法:
@Service public class StaticComponent { /** * 这里为是shiro登录时,存放登录对象信息的位置 * @return */ public String getUserId(){ Subject localSubject = ThreadContext.getSubject(); String userId = (String) localSubject.getPrincipals().getPrimaryPrincipal(); return userId; } }
测试方法:
/** * 静态Mock需要使用PowerMockRunner * 并使用PrepareForTest,该测试代表不会实际执行ThreadContext这个类 */ @RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class) @PrepareForTest({ThreadContext.class}) public class StaticComponentTest { @InjectMocks StaticComponent staticComponent; @Test public void getUserId(){ String userId = "12345"; PowerMockito.mockStatic(ThreadContext.class); Subject localSubject = PowerMockito.mock(Subject.class); when(ThreadContext.getSubject()).thenReturn(localSubject); PrincipalCollection principalCollection = PowerMockito.mock(PrincipalCollection.class); when(localSubject.getPrincipals()).thenReturn(principalCollection); when(principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal()).thenReturn("12345"); String resultUserId = staticComponent.getUserId(); Assert.assertTrue(userId.equals(resultUserId)); } }
3、方法内部有new对象的测试
@Service public class CreateComponent { @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; public MethodResult addUser(UserInfo user)throws Exception{ Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name",String.valueOf(user.getId())); map.put("email",user.getEmail()); map.put("nickname",user.getNickname()); MultiValueMap<String, String> header = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); header.put(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, Collections.singletonList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)); HttpEntity request = new HttpEntity(JSONObject.toJSONString(map), header); String url = "http://127.0.0.1:8088/add/user"; try{ ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, request, String.class); MethodResult result = JSONObject.parseObject(response.getBody(), MethodResult.class); return result; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } }
测试方法
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class) public class CreateComponentTest { @Mock private RestTemplate restTemplate; @InjectMocks private CreateComponent component; @Test public void createTest()throws Exception{ UserInfo param = new UserInfo(); param.setNickname("zhangsan"); param.setEmail("[email protected]"); param.setId(123); Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name",String.valueOf(param.getId())); map.put("email",param.getEmail()); map.put("nickname",param.getNickname()); MultiValueMap<String, String> header = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); header.put(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, Collections.singletonList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)); HttpEntity request = new HttpEntity(JSONObject.toJSONString(map), header); PowerMockito.whenNew(HttpEntity.class).withAnyArguments().thenReturn(request); ResponseEntity responseEntity = PowerMockito.mock(ResponseEntity.class); Mockito.when(restTemplate.postForEntity("http://127.0.0.1:8088/add/user",request,String.class)).thenReturn(responseEntity); MethodResult result = new MethodResult(); result.setSucceed(true); PowerMockito.when(responseEntity.getBody()).thenReturn(JSONObject.toJSONString(result)); MethodResult methodResult = component.addUser(param); Assert.assertTrue(methodResult.isSucceed()); } }
4:方法过于复杂跳过内部私有方法,再单独测试私有方法
@Service public class PrivateComponent { public Integer entranceMethod(Integer i){ methodA(i); System.out.println("call methodA end"); i = methodB(i); System.out.println("call methodB end"); i = methodC(i); System.out.println("call methodC end"); return i; } private void methodA(Integer i){ System.out.println("do methodA i = " + i); methodA2(i); } private void methodA2(Integer i){ System.out.println("do methodA2 i = " + i); } private Integer methodB(Integer i){ ++i; System.out.println("do methodB"); return i; } private Integer methodC(Integer i){ ++i; System.out.println("do methodC"); return i; } }
测试方法:
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class) @PrepareForTest(PrivateComponent.class) public class PrivateComponentTest { @InjectMocks private PrivateComponent privateComponent; /** * 测试复杂的方法,跳过方法内部的私有方法:1、该私有方法没有返回值 * @throws Exception */ @Test public void jumpPrivateMethodTest()throws Exception{ PrivateComponent component = PowerMockito.spy(privateComponent); PowerMockito.doNothing().when(component,"methodA",1); Integer i = component.entranceMethod(1); System.out.println(i); Assert.assertTrue(i == 3); } /** * 测试复杂的方法,跳过方法内部的私有方法:2、该私有方法有返回值 * @throws Exception */ @Test public void jumpPrivateMethodTest2()throws Exception{ PrivateComponent component = PowerMockito.spy(privateComponent); PowerMockito.doReturn(5).when(component,"methodB", Mockito.any()); Integer i = component.entranceMethod(1); System.out.println(i); Assert.assertTrue(i == 6); } /** * 测试复杂方法,单独测试方法内部的私有方法 * @throws Exception */ @Test public void privateMethodTest()throws Exception{ PrivateComponent component = PowerMockito.spy(privateComponent); Method method = PowerMockito.method(PrivateComponent.class,"methodB",Integer.class); Integer i = (Integer) method.invoke(component,1); System.out.println("result i = " + i); Assert.assertTrue(i == 2); } }
5、对controller进行测试
@RestController @RequestMapping("/api/user") public class AController { @Autowired private AComponent aComponent; @GetMapping(value = "/info") public UserInfo testA1(Integer id){ UserInfo userInfo = aComponent.normalMethod(id); return userInfo; } @PostMapping(value = "/update") public String updateUserInfo(@RequestBody UserInfo userInfo){ aComponent.updateUserInfo(userInfo); return "success"; } }
测试方法:
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class) public class ControllerTest { @InjectMocks private AController aController; @Mock private AComponent aComponent; private MockMvc mockMvc; @Before public void setUp() { mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(aController).build(); } /** * 使用http GET方法调用的方式来测试controller * @throws Exception */ @Test public void getControllerMvcTest() throws Exception { Integer id = 1; Mockito.when(aComponent.normalMethod(id)).thenReturn(getManUserInfo()); MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/api/user/info?id="+id)) .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()).andReturn(); String content = mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString(); Assert.assertNotNull(content); } /** * 使用http POST方法调用的方式来测试controller * @throws Exception */ @Test public void postControllerMvcTest() throws Exception { UserInfo userInfo = getManUserInfo(); MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/api/user/update") .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).content(JSON.toJSONString(userInfo))) .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()).andReturn(); String content = mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString(); Assert.assertTrue("success".equals(content)); } private UserInfo getManUserInfo(){ UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo(); userInfo.setId(1); userInfo.setUserName("zhansan"); userInfo.setAge(12); userInfo.setSex("M"); return userInfo; } }