Go 语言之 Viper 的使用
Go 语言之 Viper 的使用
Viper 介绍
Viper:https://github.com/spf13/viper
安装
go get github.com/spf13/viper
Viper 是什么?
Viper 是一个针对 Go 应用程序的完整配置解决方案,包括12-Factor 应用程序。它可以在应用程序中工作,并且可以处理所有类型的配置需求和格式。它支持:
Viper is a complete configuration solution for Go applications including 12-Factor apps. It is designed to work within an application, and can handle all types of configuration needs and formats. It supports:
- setting defaults
- reading from JSON, TOML, YAML, HCL, envfile and Java properties config files
- live watching and re-reading of config files (optional)
- reading from environment variables
- reading from remote config systems (etcd or Consul), and watching changes
- reading from command line flags
- reading from buffer
- setting explicit values
Viper can be thought of as a registry for all of your applications configuration needs.
Viper 可以被认为是满足所有应用程序配置需求的注册表。
为什么使用 Viper?
在构建现代应用程序时,您不需要担心配置文件格式; 您需要专注于构建令人满意的软件。Viper 就是为此而生的。
Viper 可以为你做以下事情:
- Find, load, and unmarshal a configuration file in JSON, TOML, YAML, HCL, INI, envfile or Java properties formats.
- Provide a mechanism to set default values for your different configuration options.
- Provide a mechanism to set override values for options specified through command line flags.
- Provide an alias system to easily rename parameters without breaking existing code.
- Make it easy to tell the difference between when a user has provided a command line or config file which is the same as the default.
Viper uses the following precedence order. Each item takes precedence over the item below it:
- explicit call to
Set - flag
- env
- config
- key/value store
- default
Important: Viper configuration keys are case insensitive. There are ongoing discussions about making that optional.
重要提示: Viper 配置键是不区分大小写的。目前正在讨论是否将其设置为可选的。
Viper 实操 Putting Values into Viper
建立默认值
一个好的配置系统将支持默认值。密钥不需要默认值,但如果没有通过配置文件、环境变量、远程配置或标志设置密钥,则默认值非常有用。
Examples:
viper.SetDefault("ContentDir", "content")
viper.SetDefault("LayoutDir", "layouts")
viper.SetDefault("Taxonomies", map[string]string{"tag": "tags", "category": "categories"})
读取配置文件
Viper 需要最小的配置,这样它就知道在哪里查找配置文件。Viper 支持 JSON、 TOML、 YAML、 HCL、 INI、 envfile 和 JavaProperties 文件。Viper 可以搜索多个路径,但目前单个 Viper 实例只支持单个配置文件。Viper 不默认任何配置搜索路径,将默认决策留给应用程序。
下面是如何使用 Viper 搜索和读取配置文件的示例。不需要任何特定的路径,但至少应该在需要配置文件的地方提供一个路径。
viper.SetConfigName("config") // name of config file (without extension)
viper.SetConfigType("yaml") // REQUIRED if the config file does not have the extension in the name
viper.AddConfigPath("/etc/appname/") // path to look for the config file in
viper.AddConfigPath("$HOME/.appname") // call multiple times to add many search paths
viper.AddConfigPath(".") // optionally look for config in the working directory
err := viper.ReadInConfig() // Find and read the config file
if err != nil { // Handle errors reading the config file
panic(fmt.Errorf("fatal error config file: %w", err))
}
您可以处理没有如下配置文件的特定情况:
if err := viper.ReadInConfig(); err != nil {
if _, ok := err.(viper.ConfigFileNotFoundError); ok {
// Config file not found; ignore error if desired
} else {
// Config file was found but another error was produced
}
}
// Config file found and successfully parsed
写入配置文件
从配置文件中读取是有用的,但有时您希望存储在运行时所做的所有修改。为此,提供了一系列命令,每个命令都有自己的用途:
- WriteConfig-将当前 viper 配置写入预定义的路径(如果存在)。如果没有预定义的路径就会出错。将覆盖当前配置文件(如果存在)。
- SafeWriteConfig-将当前 viper 配置写入预定义的路径。如果没有预定义的路径就会出错。不会覆盖当前配置文件(如果存在)。
- WriteConfigAs-将当前 viper 配置写入给定的文件路径。将覆盖给定的文件(如果存在)。
- SafeWriteConfigAs-将当前 viper 配置写入给定的文件路径。不会覆盖给定的文件(如果存在)。
As a rule of the thumb, everything marked with safe won't overwrite any file, but just create if not existent, whilst the default behavior is to create or truncate.
根据经验,所有标记为 safe 的文件都不会覆盖任何文件,只是创建(如果不存在的话) ,而默认行为是创建或截断。
A small examples section:
viper.WriteConfig() // writes current config to predefined path set by 'viper.AddConfigPath()' and 'viper.SetConfigName'
viper.SafeWriteConfig()
viper.WriteConfigAs("/path/to/my/.config")
viper.SafeWriteConfigAs("/path/to/my/.config") // will error since it has already been written
viper.SafeWriteConfigAs("/path/to/my/.other_config")
监视和重新读取配置文件
Viper 支持让应用程序在运行时实时读取配置文件的能力。
需要重新启动服务器才能使配置生效的日子已经一去不复返了,使用 viper 的应用程序可以在运行时读取配置文件的更新,而且不会错过任何一次更新。
只需告诉 viper 实例监视 Config。您还可以为 Viper 提供一个函数,以便在每次发生更改时运行该函数。
确保在调用 WatchConfig ()之前添加了所有的 configPath
viper.OnConfigChange(func(e fsnotify.Event) {
fmt.Println("Config file changed:", e.Name)
})
viper.WatchConfig()
配置文件实时加载实操
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
)
func main() {
// 设置默认值
viper.SetDefault("fileDir", "./")
// 读取配置文件
viper.SetConfigFile("./config.yaml") // 指定配置文件路径
viper.SetConfigName("config") // 配置文件名称(无扩展名)
viper.SetConfigType("yaml") // 如果配置文件的名称中没有扩展名,则需要配置此项
viper.AddConfigPath("/etc/appname/") // 查找配置文件所在的路径
viper.AddConfigPath("$HOME/.appname") // 多次调用以添加多个搜索路径
viper.AddConfigPath(".") // 还可以在工作目录中查找配置
err := viper.ReadInConfig() // 查找并读取配置文件
if err != nil { // 处理读取配置文件的错误
panic(fmt.Errorf("Fatal error config file: %s \n", err))
}
// 实时监控配置文件的变化 WatchConfig 开始监视配置文件的更改。
viper.WatchConfig()
// OnConfigChange设置配置文件更改时调用的事件处理程序。
// 当配置文件变化之后调用的一个回调函数
viper.OnConfigChange(func(e fsnotify.Event) {
fmt.Println("Config file changed:", e.Name)
})
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/version", func(c *gin.Context) {
// GetString以字符串的形式返回与键相关的值。
c.String(http.StatusOK, viper.GetString("version"))
})
r.Run()
}
运行并访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/version
Code/go/viper_demo via 🐹 v1.20.3 via 🅒 base
➜ go run main.go
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] GET /version --> main.main.func2 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] You trusted all proxies, this is NOT safe. We recommend you to set a value.
Please check https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-don-t-trust-all-proxies for details.
[GIN-debug] Environment variable PORT is undefined. Using port :8080 by default
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8080
[GIN] 2023/06/18 - 11:42:10 | 200 | 39.5µs | 127.0.0.1 | GET "/version"
[GIN] 2023/06/18 - 11:42:10 | 404 | 750ns | 127.0.0.1 | GET "/favicon.ico"
Config file changed: /Users/qiaopengjun/Code/go/viper_demo/config.yaml
[GIN] 2023/06/18 - 11:43:41 | 200 | 17.459µs | 127.0.0.1 | GET "/version"
config.yaml
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 8080
version: "v0.0.2"
mysql:
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 3306
dbname: "sql_demo"
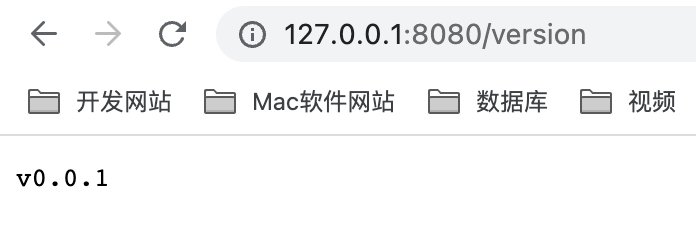
运行之后,访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/version。此时结果返回 v0.0.1
修改 config.yaml 文件中的version为 "v0.0.2"后,控制台输出 Config file changed: /Users/qiaopengjun/Code/go/viper_demo/config.yaml 。配置文件实时加载,访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/version。此时结果返回 v0.0.2。

从 io.Reader 读取配置
Viper 预定义了许多配置源,例如文件、环境变量、标志和远程 K/V 存储,但是您并不绑定到它们。您还可以实现自己所需的配置源,并将其提供给 viper。
viper.SetConfigType("yaml") // or viper.SetConfigType("YAML")
// any approach to require this configuration into your program.
var yamlExample = []byte(`
Hacker: true
name: steve
hobbies:
- skateboarding
- snowboarding
- go
clothing:
jacket: leather
trousers: denim
age: 35
eyes : brown
beard: true
`)
viper.ReadConfig(bytes.NewBuffer(yamlExample))
viper.Get("name") // this would be "steve"
设置覆盖
它们可以来自命令行标志,也可以来自您自己的应用程序逻辑。
viper.Set("Verbose", true)
viper.Set("LogFile", LogFile)
注册和使用别名
别名允许多个键引用单个值
viper.RegisterAlias("loud", "Verbose")
viper.Set("verbose", true) // same result as next line
viper.Set("loud", true) // same result as prior line
viper.GetBool("loud") // true
viper.GetBool("verbose") // true
使用环境变量
Viper 完全支持环境变量。这使12-Factor apps开箱即用。有五种方法可以帮助 ENV 的工作:
AutomaticEnv()BindEnv(string...) : errorSetEnvPrefix(string)SetEnvKeyReplacer(string...) *strings.ReplacerAllowEmptyEnv(bool)
当使用 ENV 变量时,重要的是要认识到 Viper 将 ENV 变量视为区分大小写的。
Viper 提供了一种机制来尝试确保 ENV 变量是唯一的。通过使用 SetEnvPrefix,可以告诉 Viper 在读取环境变量时使用前缀。BindEnv 和 AutomaticEnv 都将使用此前缀。
BindEnv 接受一个或多个参数。第一个参数是键名,其余的是要绑定到这个键的环境变量的名称。如果提供了多个,它们将按照指定的顺序优先。环境变量的名字是区分大小写的。如果没有提供 ENV 变量名,那么 Viper 将自动假定 ENV 变量匹配以下格式: 前缀 + “ _”+ ALL CAPS 中的键名。当显式提供 ENV 变量名(第二个参数)时,它不会自动添加前缀。例如,如果第二个参数是“ ID”,Viper 将查找 ENV 变量“ ID”。
使用 ENV 变量时需要注意的一点是,每次访问该值时都会读取它。当调用 BindEnv 时,Viper 不会修复该值。
AutomaticEnv 是一个强大的助手,特别是当与 SetEnvPrefix 组合时。当召唤时,Viper会随时检查是否有环境变量。请求已经提出。它将适用以下规则。如果设置了大写和前缀为 EnvPrefix 的键,它将检查是否有名称与之匹配的环境变量。
SetEnvKeyReplace 允许您使用字符串。对象重写一定范围内的 Env 键。如果您希望在 Get ()调用中使用-或其他内容,但希望环境变量使用 _ 分隔符,那么这很有用。在viper_test.go 中可以找到使用它的示例。
或者,您可以使用带有 NewWithOptions 工厂函数的 EnvKeyReplace。与 SetEnvKeyReplace 不同,它接受 StringReplace 接口,允许您编写自定义字符串替换逻辑。
默认情况下,空环境变量被认为是未设置的,并将回退到下一个配置源。若要将空环境变量视为设置,请使用 AllowEmptyEnv 方法。
Env example
SetEnvPrefix("spf") // will be uppercased automatically
BindEnv("id")
os.Setenv("SPF_ID", "13") // typically done outside of the app
id := Get("id") // 13
Flags 的使用
Viper 具有绑定到标志的能力。具体来说,Viper 支持在 Cobra 库中使用的 Pflags。
与 BindEnv 一样,该值不是在调用绑定方法时设置的,而是在访问该方法时设置的。这意味着您可以尽早进行绑定,即使在 init ()函数中也是如此。
对于单个标志,BindPFlag ()方法提供了此功能。
Example:
serverCmd.Flags().Int("port", 1138, "Port to run Application server on")
viper.BindPFlag("port", serverCmd.Flags().Lookup("port"))
您还可以绑定一组现有的 pFlag (pFlag. FlagSet) :
Example:
pflag.Int("flagname", 1234, "help message for flagname")
pflag.Parse()
viper.BindPFlags(pflag.CommandLine)
i := viper.GetInt("flagname") // retrieve values from viper instead of pflag
在 Viper 中使用 pFlag 并不排除在其它包使用标准库中 flag package。 pflag 包可以通过导入这些flag 来处理为flag 包定义的flags。这是通过调用一个名为 AddGoFlagSet ()的 pFlag 包提供的便利函数来实现的。
Example:
package main
import (
"flag"
"github.com/spf13/pflag"
)
func main() {
// using standard library "flag" package
flag.Int("flagname", 1234, "help message for flagname")
pflag.CommandLine.AddGoFlagSet(flag.CommandLine)
pflag.Parse()
viper.BindPFlags(pflag.CommandLine)
i := viper.GetInt("flagname") // retrieve value from viper
// ...
}
Flag interfaces
Viper 提供了两个 Go 接口来绑定其他标志系统,如果你不使用标志的话。
FlagValue 表示一个标志,这是一个关于如何实现这个接口的非常简单的例子:
type myFlag struct {}
func (f myFlag) HasChanged() bool { return false }
func (f myFlag) Name() string { return "my-flag-name" }
func (f myFlag) ValueString() string { return "my-flag-value" }
func (f myFlag) ValueType() string { return "string" }
一旦你的标志实现了这个接口,你可以简单地告诉 Viper 绑定它:
viper.BindFlagValue("my-flag-name", myFlag{})
FlagValueSet represents a group of flags. 这是一个关于如何实现这个接口的非常简单的例子:
type myFlagSet struct {
flags []myFlag
}
func (f myFlagSet) VisitAll(fn func(FlagValue)) {
for _, flag := range flags {
fn(flag)
}
}
Once your flag set implements this interface, you can simply tell Viper to bind it:
fSet := myFlagSet{
flags: []myFlag{myFlag{}, myFlag{}},
}
viper.BindFlagValues("my-flags", fSet)
Remote Key/Value Store Support 远程 Key/Value 存储支持
要在 Viper 中启用远程支持,请对 Viper/remote 包执行匿名导入:
import _ "github.com/spf13/viper/remote"
Viper 将读取从 Key/Value 存储(如 etcd 或 Consule)中的路径检索到的配置字符串(如 JSON、 TOML、 YAML、 HCL 或 envfile)。这些值优先于默认值,但是被从磁盘、标志或环境变量检索到的配置值覆盖。
Viper 使用 crypt 从 K/V 存储中检索配置,这意味着您可以存储加密的配置值,如果您有正确的 gpg 密钥环,则可以自动解密它们。加密是可选的。
您可以将远程配置与本地配置结合使用,也可以独立于本地配置使用。
crypt 有一个命令行助手,您可以使用它在 K/V 存储中放置配置。在 http://127.0.0.1:4001上,crypt 默认为 etcd。
$ go get github.com/bketelsen/crypt/bin/crypt
$ crypt set -plaintext /config/hugo.json /Users/hugo/settings/config.json
Confirm that your value was set:
$ crypt get -plaintext /config/hugo.json
有关如何设置加密值或如何使用 Consul 的示例,请参见 crypt 文档。
Remote Key/Value Store Example - Unencrypted 远程Key/Value存储示例-未加密
etcd
viper.AddRemoteProvider("etcd", "http://127.0.0.1:4001","/config/hugo.json")
viper.SetConfigType("json") // because there is no file extension in a stream of bytes, supported extensions are "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "env", "dotenv"
err := viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
etcd3
viper.AddRemoteProvider("etcd3", "http://127.0.0.1:4001","/config/hugo.json")
viper.SetConfigType("json") // because there is no file extension in a stream of bytes, supported extensions are "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "env", "dotenv"
err := viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
Consul
You need to set a key to Consul key/value storage with JSON value containing your desired config. For example, create a Consul key/value store key MY_CONSUL_KEY with value:
您需要使用包含所需配置的 JSON 值将一个键设置为 Consul key/value 存储。例如,创建一个 Consul key/value store key MY _ CONSUL _ KEY,其值为:
{
"port": 8080,
"hostname": "myhostname.com"
}
viper.AddRemoteProvider("consul", "localhost:8500", "MY_CONSUL_KEY")
viper.SetConfigType("json") // Need to explicitly set this to json
err := viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
fmt.Println(viper.Get("port")) // 8080
fmt.Println(viper.Get("hostname")) // myhostname.com
Firestore
viper.AddRemoteProvider("firestore", "google-cloud-project-id", "collection/document")
viper.SetConfigType("json") // Config's format: "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml"
err := viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
当然,您也可以使用 SecureRemoteProvider
Remote Key/Value Store Example - Encrypted 远程Key/Value存储示例-加密
viper.AddSecureRemoteProvider("etcd","http://127.0.0.1:4001","/config/hugo.json","/etc/secrets/mykeyring.gpg")
viper.SetConfigType("json") // because there is no file extension in a stream of bytes, supported extensions are "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "env", "dotenv"
err := viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
Watching Changes in etcd - Unencrypted 监听etcd 中的更改-未加密
// alternatively, you can create a new viper instance.
var runtime_viper = viper.New()
runtime_viper.AddRemoteProvider("etcd", "http://127.0.0.1:4001", "/config/hugo.yml")
runtime_viper.SetConfigType("yaml") // because there is no file extension in a stream of bytes, supported extensions are "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "env", "dotenv"
// read from remote config the first time.
err := runtime_viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
// unmarshal config 反序列化
runtime_viper.Unmarshal(&runtime_conf)
// open a goroutine to watch remote changes forever
go func(){
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 5) // delay after each request
// currently, only tested with etcd support
err := runtime_viper.WatchRemoteConfig()
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("unable to read remote config: %v", err)
continue
}
// unmarshal new config into our runtime config struct. you can also use channel
// to implement a signal to notify the system of the changes
runtime_viper.Unmarshal(&runtime_conf)
}
}()
从 Viper 获取值
在 Viper 中,有几种根据值的类型获取值的方法。现有以下职能和方法:
Get(key string) : interface{}GetBool(key string) : boolGetFloat64(key string) : float64GetInt(key string) : intGetIntSlice(key string) : []intGetString(key string) : stringGetStringMap(key string) : map[string]interface{}GetStringMapString(key string) : map[string]stringGetStringSlice(key string) : []stringGetTime(key string) : time.TimeGetDuration(key string) : time.DurationIsSet(key string) : boolAllSettings() : map[string]interface{}
需要注意的一点是,如果没有找到,每个 Get 函数将返回一个零值。为了检查给定的键是否存在,提供了 IsSet ()方法。
Example:
viper.GetString("logfile") // case-insensitive Setting & Getting
if viper.GetBool("verbose") {
fmt.Println("verbose enabled")
}
Accessing nested keys 访问嵌套键
访问器方法还接受深度嵌套键的格式化路径。例如,如果加载了以下 JSON 文件:
{
"host": {
"address": "localhost",
"port": 5799
},
"datastore": {
"metric": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3099
},
"warehouse": {
"host": "198.0.0.1",
"port": 2112
}
}
}
Viper 可以通过传递.分隔的键路径来访问嵌套字段:
GetString("datastore.metric.host") // (returns "127.0.0.1")
这符合上面建立的优先级规则; 对路径的搜索将通过剩余的配置注册中心级联,直到找到。
例如,给定这个配置文件,datastore.metric.host 和 datastore.metric.port 都已经定义(并且可能被覆盖)。如果在默认情况下另外定义了 datastore.metric.protocol,Viper 也会找到它。
但是,如果 datastore.metrics 被覆盖(通过一个标志、一个环境变量、 Set ()方法,...)并且有一个立即的值,那么 datastore.metrics 的所有子键都将变得未定义,它们将被更高优先级的配置级别“隐藏”。
Viper 可以通过路径中的数字访问数组索引。例如:
{
"host": {
"address": "localhost",
"ports": [
5799,
6029
]
},
"datastore": {
"metric": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3099
},
"warehouse": {
"host": "198.0.0.1",
"port": 2112
}
}
}
GetInt("host.ports.1") // returns 6029
最后,如果存在与分隔的键路径匹配的键,则将返回其值。
{
"datastore.metric.host": "0.0.0.0",
"host": {
"address": "localhost",
"port": 5799
},
"datastore": {
"metric": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3099
},
"warehouse": {
"host": "198.0.0.1",
"port": 2112
}
}
}
GetString("datastore.metric.host") // returns "0.0.0.0"
提取子树
在开发可重用模块时,提取配置的子集并将其传递给模块通常很有用。通过这种方式,可以使用不同的配置多次实例化模块。
例如,应用程序可能为不同目的使用多个不同的缓存存储区:
cache:
cache1:
max-items: 100
item-size: 64
cache2:
max-items: 200
item-size: 80
我们可以将缓存名传递给一个模块(例如。NewCache (“ cache1”) ,但是访问配置键需要奇怪的连接,并且与全局配置的分离程度较低。
因此,与其这样做,不如将 Viper 实例传递给代表配置子集的构造函数:
cache1Config := viper.Sub("cache.cache1")
if cache1Config == nil { // Sub returns nil if the key cannot be found
panic("cache configuration not found")
}
cache1 := NewCache(cache1Config)
注意: 始终检查 Sub 的返回值。如果找不到键,它会返回 nil。
在内部,NewCache 函数可以直接处理 max-item 和 item-size 键:
func NewCache(v *Viper) *Cache {
return &Cache{
MaxItems: v.GetInt("max-items"),
ItemSize: v.GetInt("item-size"),
}
}
产生的代码很容易测试,因为它与主配置结构解耦,并且出于同样的原因更容易重用。
Unmarshaling 反序列化
您还可以选择将所有值或特定值反序列化到结构体、map等。
有两种方法可以做到这一点:
Unmarshal(rawVal interface{}) : errorUnmarshalKey(key string, rawVal interface{}) : error
Example:
type config struct {
Port int
Name string
PathMap string `mapstructure:"path_map"`
}
var C config
err := viper.Unmarshal(&C)
if err != nil {
t.Fatalf("unable to decode into struct, %v", err)
}
如果要反序列化键本身包含点(默认的键分隔符)的配置,必须更改分隔符:
v := viper.NewWithOptions(viper.KeyDelimiter("::"))
v.SetDefault("chart::values", map[string]interface{}{
"ingress": map[string]interface{}{
"annotations": map[string]interface{}{
"traefik.frontend.rule.type": "PathPrefix",
"traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect": "true",
},
},
})
type config struct {
Chart struct{
Values map[string]interface{}
}
}
var C config
v.Unmarshal(&C)
Viper 还支持将数据解析为嵌入式结构:
/*
Example config:
module:
enabled: true
token: 89h3f98hbwf987h3f98wenf89ehf
*/
type config struct {
Module struct {
Enabled bool
moduleConfig `mapstructure:",squash"`
}
}
// moduleConfig could be in a module specific package
type moduleConfig struct {
Token string
}
var C config
err := viper.Unmarshal(&C)
if err != nil {
t.Fatalf("unable to decode into struct, %v", err)
}
Viper 使用底层 github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure 来解析值,默认情况下使用 mapstructure。
实操
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
)
type Config struct {
Host string `mapstructure:"host"`
Version string `mapstructure:"version"`
Port int `mapstructure:"port"`
MySQLConfig `mapstructure:"mysql"`
}
type MySQLConfig struct {
Host string `mapstructure:"host"`
DbName string `mapstructure:"dbname"`
Port int `mapstructure:"port"`
}
func main() {
// 设置默认值
viper.SetDefault("fileDir", "./")
// 读取配置文件
viper.SetConfigFile("./config.yaml") // 指定配置文件路径
viper.SetConfigName("config") // 配置文件名称(无扩展名)
viper.SetConfigType("yaml") // 如果配置文件的名称中没有扩展名,则需要配置此项
viper.AddConfigPath("/etc/appname/") // 查找配置文件所在的路径
viper.AddConfigPath("$HOME/.appname") // 多次调用以添加多个搜索路径
viper.AddConfigPath(".") // 还可以在工作目录中查找配置
err := viper.ReadInConfig() // 查找并读取配置文件
if err != nil { // 处理读取配置文件的错误
panic(fmt.Errorf("Fatal error config file: %s \n", err))
}
// 实时监控配置文件的变化 WatchConfig 开始监视配置文件的更改。
viper.WatchConfig()
// OnConfigChange设置配置文件更改时调用的事件处理程序。
// 当配置文件变化之后调用的一个回调函数
viper.OnConfigChange(func(e fsnotify.Event) {
fmt.Println("Config file changed:", e.Name)
})
//r := gin.Default()
//r.GET("/version", func(c *gin.Context) {
// // GetString以字符串的形式返回与键相关的值。
// c.String(http.StatusOK, viper.GetString("version"))
//})
//r.Run()
var c Config
if err := viper.Unmarshal(&c); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("viper Unmarshal failed, err: %v\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("viper unmarshal success. c: %#v\n", c)
}
config.yaml
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 8080
version: "v0.0.2"
mysql:
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 3306
dbname: "sql_demo"
运行
Code/go/viper_demo via 🐹 v1.20.3 via 🅒 base
➜ go run main.go
viper unmarshal success. c: main.Config{Host:"127.0.0.1", Version:"v0.0.2", Port:8080, MySQLConfig:main.MySQLConfig{Host:"127.0.0.1", DbName:"sql_demo", Port:3306}}
Code/go/viper_demo via 🐹 v1.20.3 via 🅒 base
➜
Decoding custom formats
Viper 经常需要的一个特性是添加更多的值格式和解码器。例如,解析字符(点、逗号、分号等)将字符串分隔成片。
这在使用映射结构解码钩子的 Viper 中已经可用。
阅读更多关于 this blog post.。
Marshalling to string 序列化成字符串
您可能需要将 viper 中保存的所有设置编组成一个字符串,而不是将它们写入文件。您可以对 AllSettings ()返回的配置使用您喜欢的格式的编组器。
import (
yaml "gopkg.in/yaml.v2"
// ...
)
func yamlStringSettings() string {
c := viper.AllSettings()
bs, err := yaml.Marshal(c)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("unable to marshal config to YAML: %v", err)
}
return string(bs)
}
Viper or Vipers? 单个和多个 Viper 的选择
Viper已经准备好开箱使用了。开始使用 Viper 不需要配置或初始化。由于大多数应用程序都希望使用单个中央存储库进行配置,因此 viper 包提供了这一功能。它类似于单例模式。
在上面的所有示例中,它们都演示了如何在单例样式方法中使用 viper
多个 Viper 的使用
您还可以创建许多不同的vipers在您的应用程序中使用。每一个都有自己独特的一组配置和值。每个都可以从不同的配置文件、键值存储等读取。Viper 包支持的所有功能都反映为 viper 上的方法。
Example:
x := viper.New()
y := viper.New()
x.SetDefault("ContentDir", "content")
y.SetDefault("ContentDir", "foobar")
//...
在处理多条vipers时,由用户来跟踪不同的vipers。
更多详情请阅读:https://github.com/spf13/viper/blob/master/README.md
本文来自博客园,作者:寻月隐君,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/QiaoPengjun/p/17489207.html