鸿蒙HarmonyOS实战-Stage模型(信息传递载体Want)
🚀前言
应用中的信息传递是为了实现各种功能和交互。信息传递可以帮助用户和应用之间进行有效的沟通和交流。通过信息传递,应用可以向用户传递重要的消息、通知和提示,以提供及时的反馈和指导。同时,用户也可以通过信息传递向应用发送指令、请求和反馈,以实现个性化的需求和操作。
信息传递还可以帮助应用之间实现数据的共享和交互。通过信息传递,不同应用可以实现数据的互通,以实现更多的功能和服务。例如,一个购物应用可以通过信息传递与支付应用进行数据交互,以实现支付功能;一个社交媒体应用可以通过信息传递与地图应用进行数据交互,以实现位置分享功能。
此外,信息传递还可以帮助应用之间实现联动和协作。通过信息传递,应用可以实现多个功能的组合和协同,以提供更加丰富和综合的服务。例如,一个音乐应用可以与闹钟应用进行信息传递,以实现在特定时间播放特定的音乐。
🚀一、信息传递载体Want
🔎1.Want概述
🦋1.1 Want的定义与用途
HarmonyOS中的"Want"是一个用于定义和控制应用程序之间通信的基本概念。它可以用来描述一个应用程序对某个特定操作的需求或意愿,比如获取某个设备的位置信息、访问某个传感器的数据等。
使用"Want"可以实现应用程序之间的无缝协作和互操作。通过定义和使用"Wants",应用程序可以根据自身的需求发送请求,并且可以接收和处理其他应用程序发送的请求。这种机制能够促进应用程序之间的交互和共享,并且使得整个系统更加智能和高效。
"Wants"的使用可以带来许多好处。首先,它可以简化应用程序之间的通信和协作,减少开发人员的工作量。其次,它可以增强系统的灵活性和可扩展性,使得应用程序能够动态地适应不同的环境和设备。最后,它可以提供更加个性化和智能化的用户体验,使得应用程序能够更好地理解用户的需求并作出相应的反应。

🦋1.2 Want的类型
在HarmonyOS中,信息传递载体Want的类型可以分为两种:显式Want和隐式Want。
显式Want:显式Want是指明确指定要操作的组件或服务的Want。通过显式Want,可以精确地指定要传递给目标组件或服务的信息,并指定具体的要执行的操作。显式Want会包含组件名和操作类型等明确的指令信息。例如,可以使用显式Want来启动指定的Activity或调用指定的服务。
let wantInfo = {
deviceId: '', // deviceId为空表示本设备
bundleName: 'com.example.myapplication',
abilityName: 'FuncAbility',
}
隐式Want:隐式Want是指不明确指定要操作的组件或服务的Want,而是根据一定的规则和条件来进行匹配。通过隐式Want,可以实现组件之间的解耦和灵活性。隐式Want一般包含一组动作、类别、数据类型等条件,系统会根据这些条件来匹配合适的组件或服务。例如,可以使用隐式Want来处理某个特定类型的数据或根据某个特定的动作执行相应的操作。
let wantInfo = {
// uncomment line below if wish to implicitly query only in the specific bundle.
// bundleName: 'com.example.myapplication',
action: 'ohos.want.action.search',
// entities can be omitted
entities: [ 'entity.system.browsable' ],
uri: 'https://www.test.com:8080/query/student',
type: 'text/plain',
};
🔎2.显式Want与隐式Want匹配规则
🦋2.1 隐式Want匹配原理详解
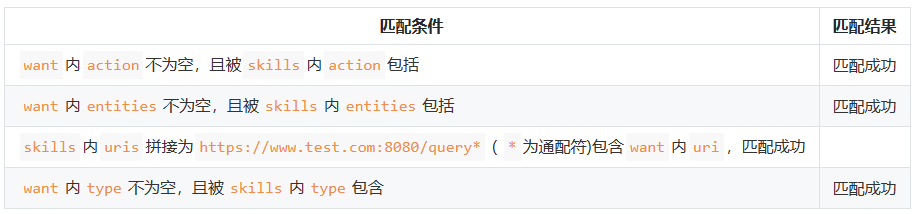
系统将调用方传入的want参数(包含action、entities、uri和type属性)与已安装待匹配的应用Ability的skills配置(包含actions、entities、uris和type属性)依次进行匹配。当四个属性匹配均通过,则此应用才会被应用选择器展示给用户进行选择。
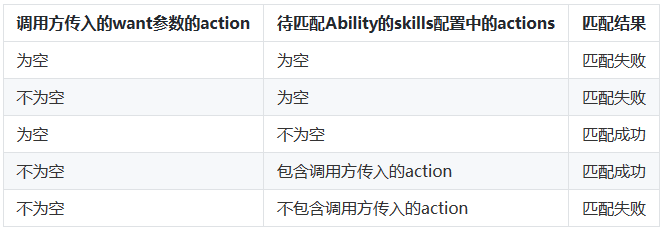
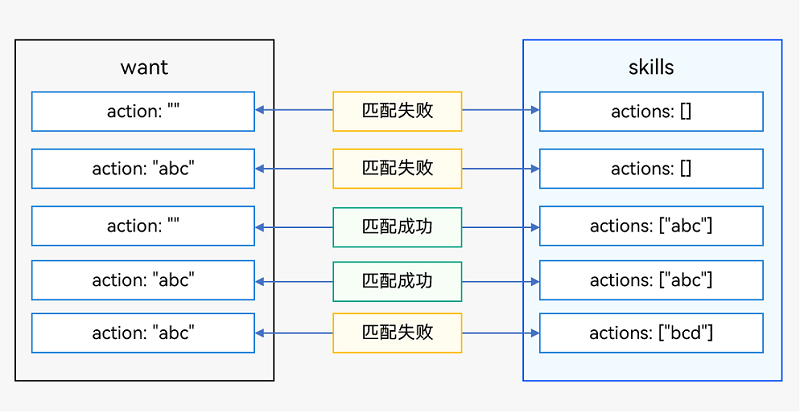
☀️2.1.1 want参数的action匹配规则
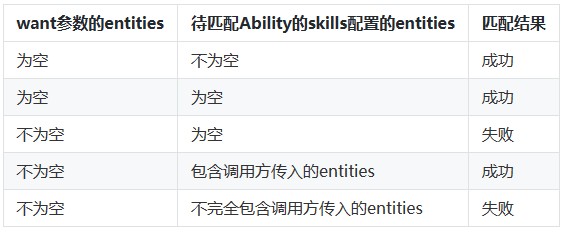
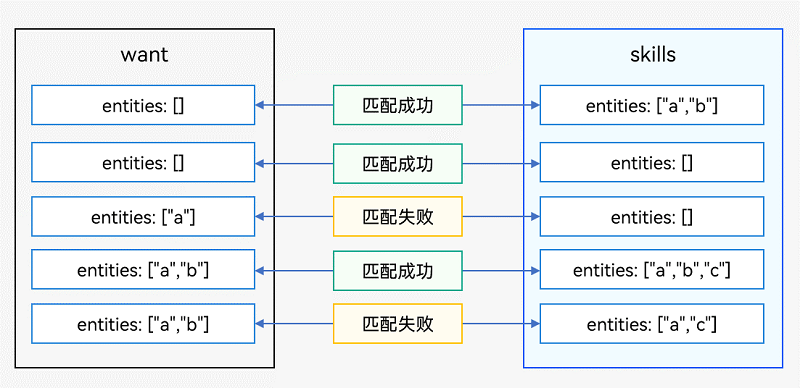
☀️2.1.2 want参数的entities匹配规则
☀️2.1.3 want参数的uri和type匹配规则
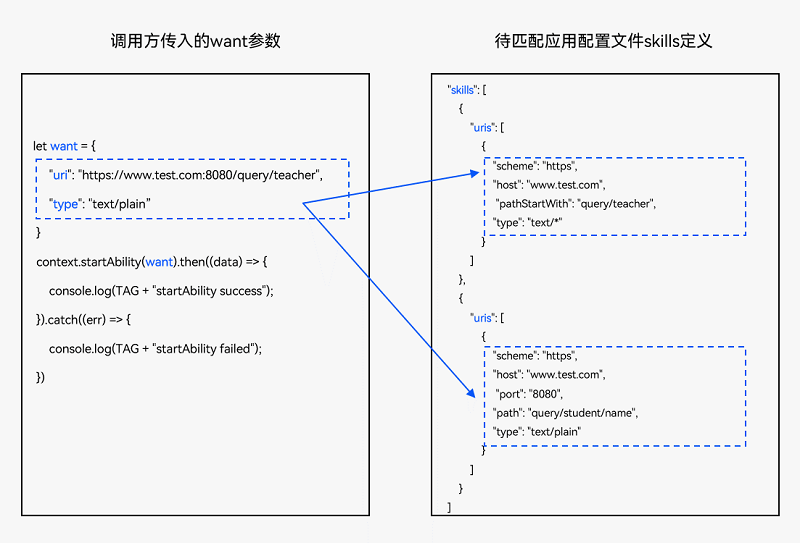
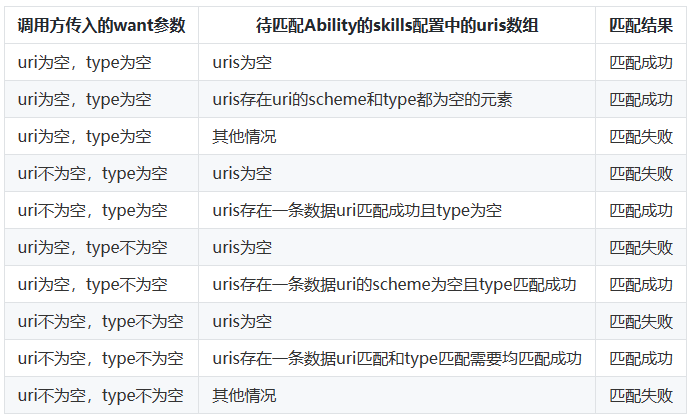
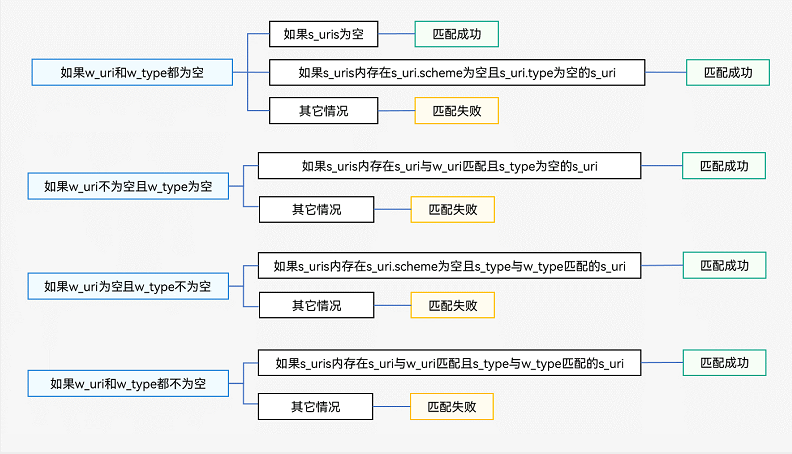
☀️2.1.4 uri匹配规则
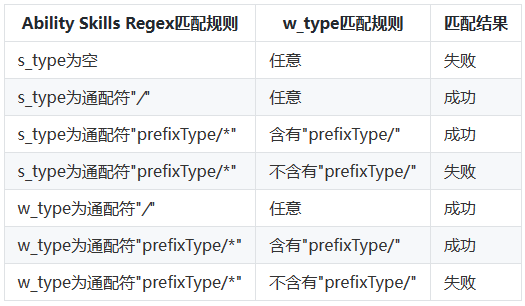
以下是根据给定匹配规则展示的表格:
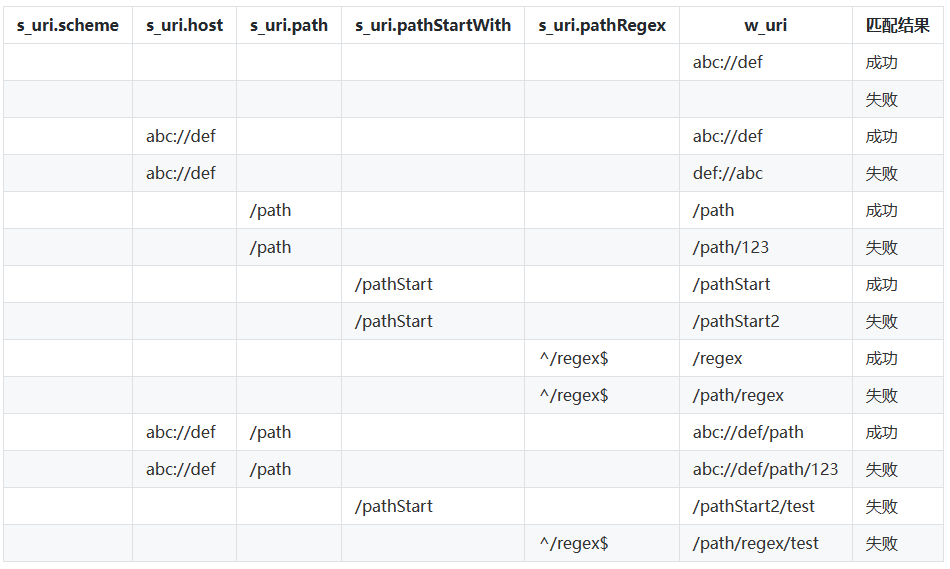
待匹配Ability的skills配置的uris中scheme、host、port、path、pathStartWith和pathRegex属性拼接,如果依次声明了path、pathStartWith和pathRegex属性时,uris将分别拼接为如下三种表达式:
-
全路径表达式:scheme://host:port/path
-
前缀表达式:scheme://host:port/pathStartWith
-
正则表达式:scheme://host:port/pathRegex
☀️2.1.5 type匹配规则
🔎3.常见action与entities
🦋3.1 action
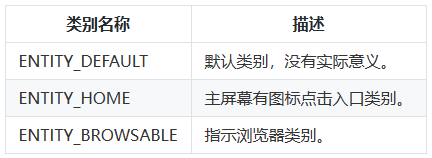
表示调用方要执行的通用操作(如查看、分享、应用详情)

🦋3.2 entities
表示目标Ability的类别信息(如浏览器、视频播放器)
🔎4.使用显式Want启动Ability
1、启动方
新建callerAbility
2、被启动方
同理新建calleeAbility
3、启动方UI
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'callerAbility'
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text('hello')
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
// A new button with will call explicitStartAbility() when clicked.
Button("CLICKME")
.onClick(this.explicitStartAbility) // explicitStartAbility见下面示例代码
// ...
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
async explicitStartAbility() {
try {
// Explicit want with abilityName specified.
let want = {
deviceId: "",
bundleName: "com.example.myapplication",
abilityName: "calleeAbility"
};
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
await context.startAbility(want);
console.info(`explicit start ability succeed`);
} catch (error) {
console.info(`explicit start ability failed with ${error.code}`);
}
}
}
4、执行
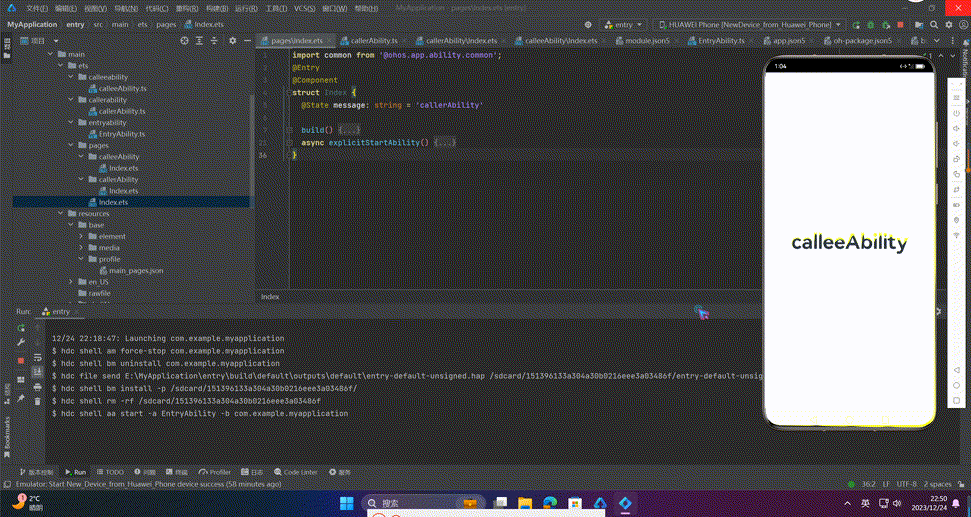
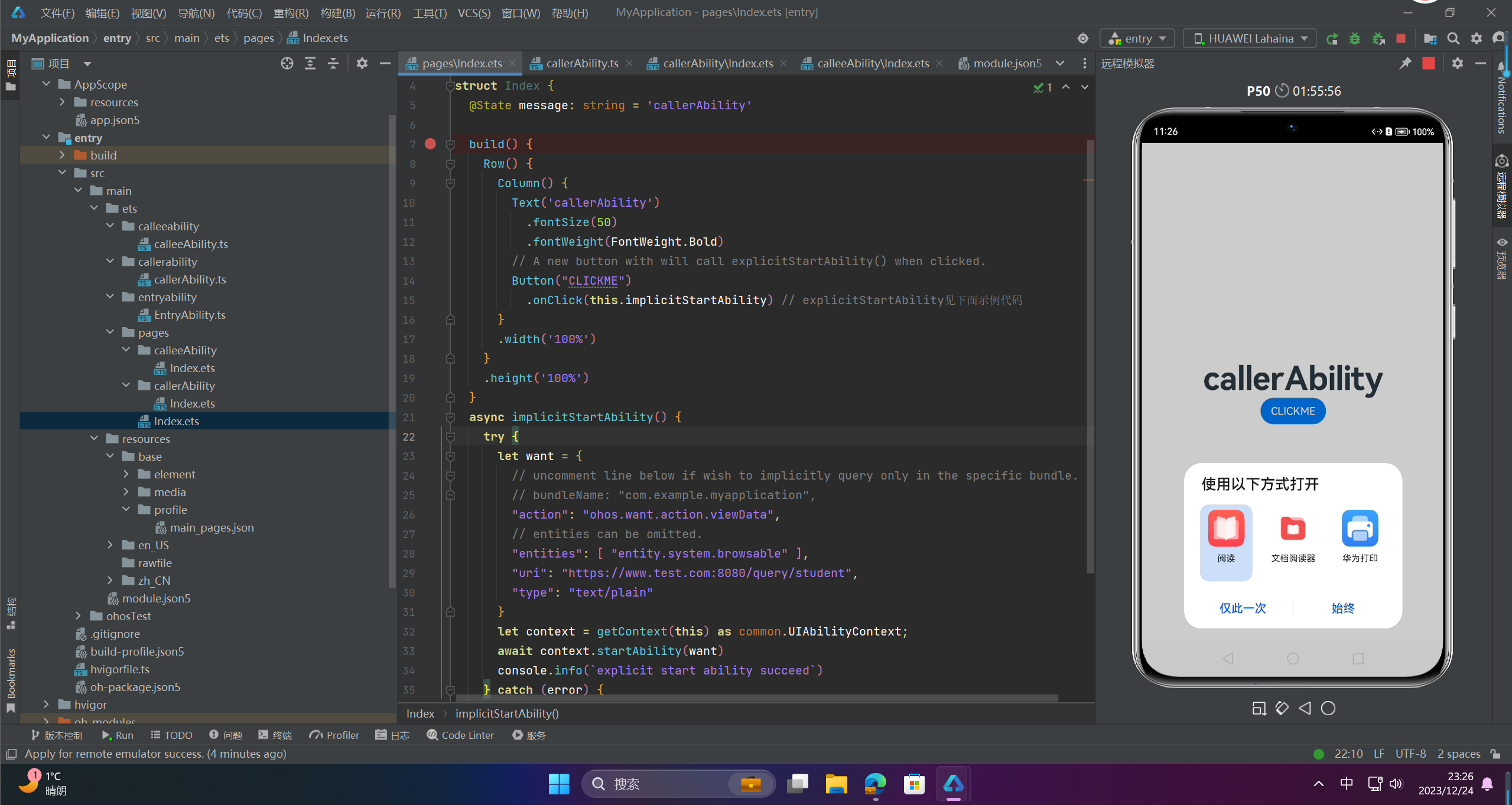
🔎5.使用隐式Want打开网址
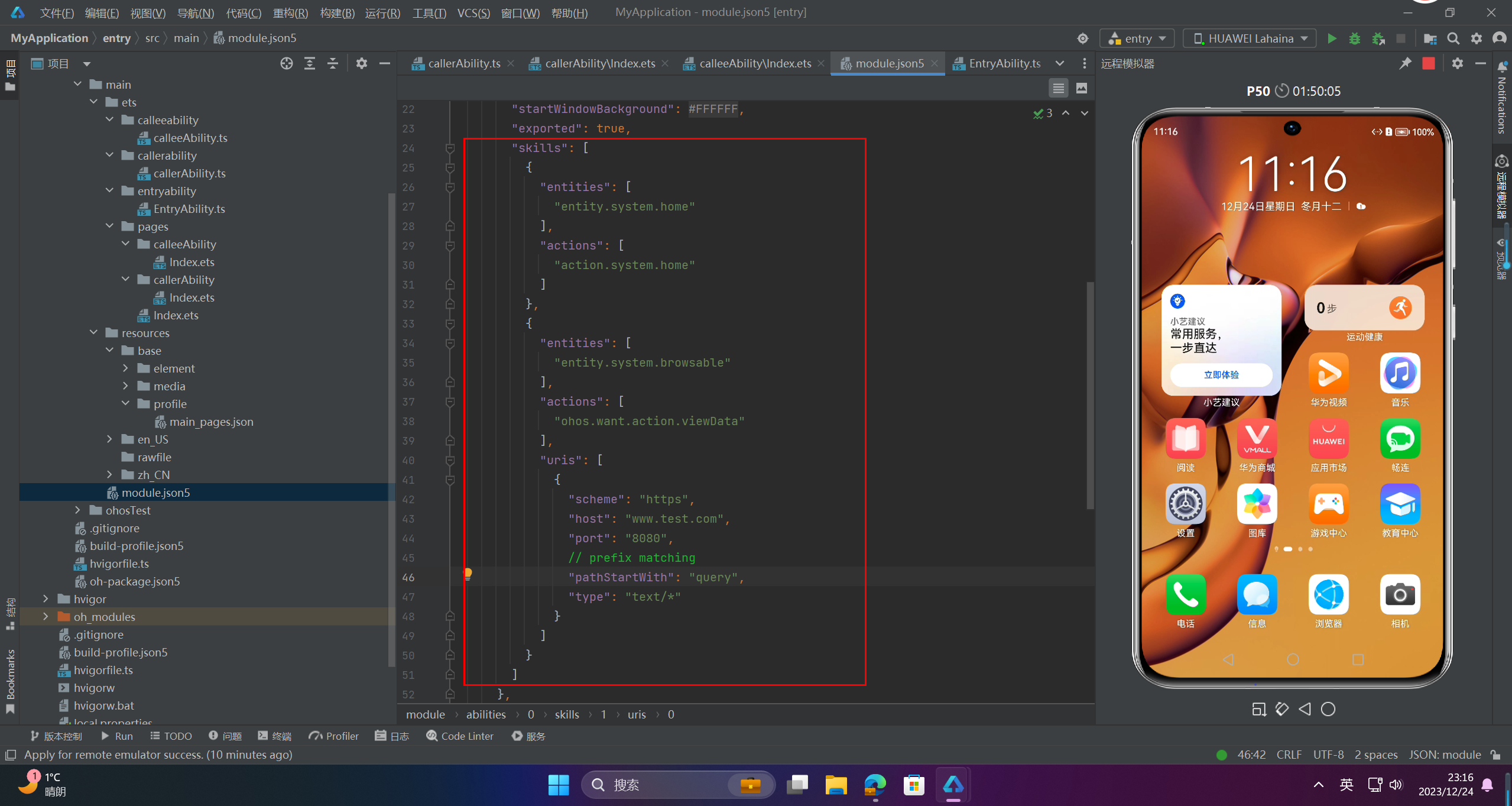
1、module.json5配置
"skills": [
{
"entities": [
"entity.system.browsable"
// ...
],
"actions": [
"ohos.want.action.viewData"
// ...
],
"uris": [
{
"scheme": "https",
"host": "www.test.com",
"port": "8080",
// prefix matching
"pathStartWith": "query",
"type": "text/*"
},
{
"scheme": "http",
// ...
}
// ...
]
},
]
2、定义跳转函数
async implicitStartAbility() {
try {
let want = {
// uncomment line below if wish to implicitly query only in the specific bundle.
// bundleName: "com.example.myapplication",
"action": "ohos.want.action.viewData",
// entities can be omitted.
"entities": [ "entity.system.browsable" ],
"uri": "https://www.test.com:8080/query/student",
"type": "text/plain"
}
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
await context.startAbility(want)
console.info(`explicit start ability succeed`)
} catch (error) {
console.info(`explicit start ability failed with ${error.code}`)
}
}
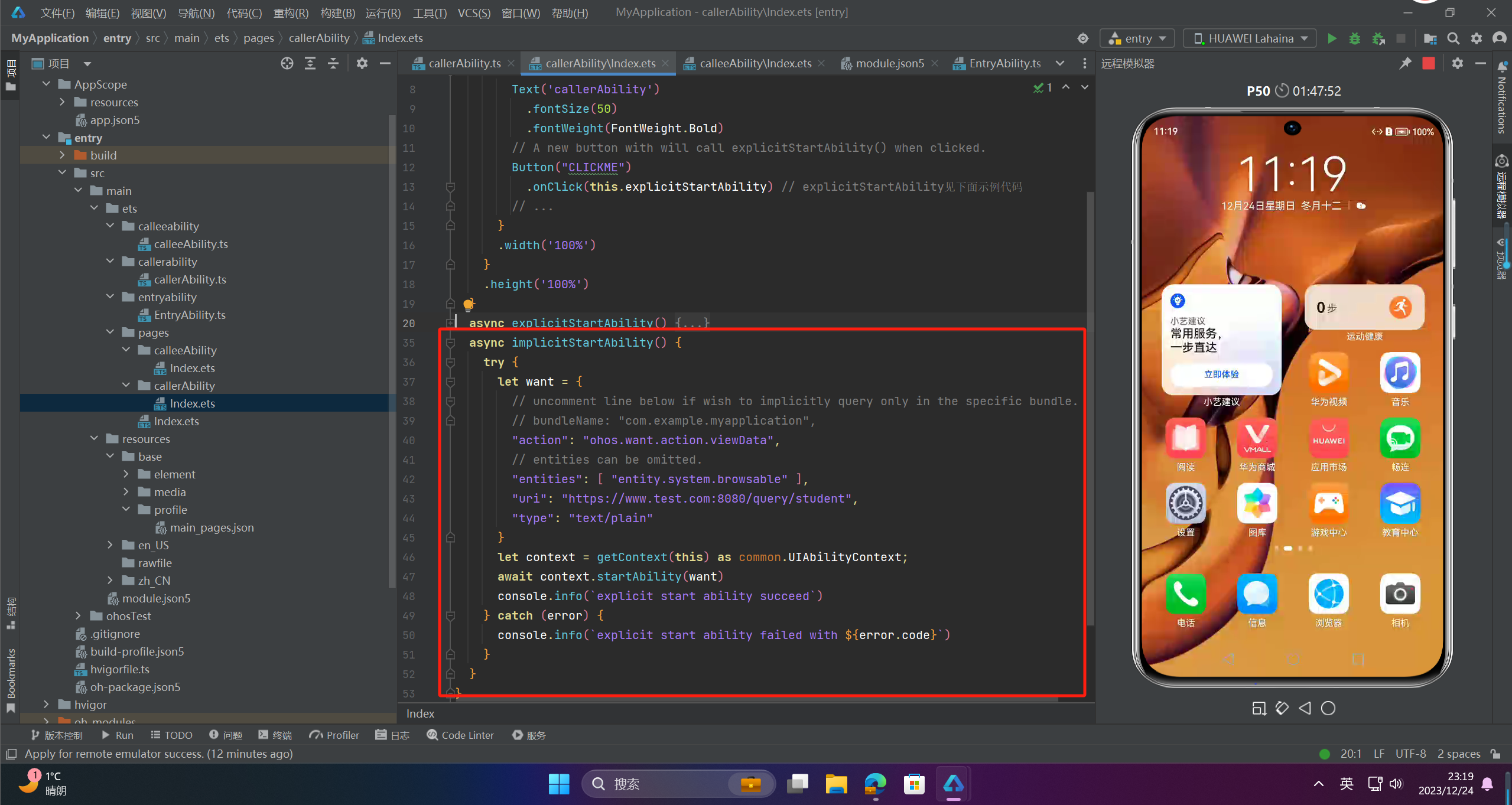
3、运行
🔎6.应用间使用Want分享数据
1、分享方
读取文件
import fileIO from '@ohos.fileio';
// let path = ...
// file open where path is a variable contains the file path.
let fileFd = fileIO.openSync(path, 0o102, 0o666);
传输文件信息构造
import wantConstant from '@ohos.ability.wantConstant';
// let path = ...
// let fileFd = ...
// let fileSize = ...
let want = {
// This action is used to implicitly match the application selctor.
action: wantConstant.Action.ACTION_SELECT,
// This is the custom parameter in the first layer of want
// which is intended to add info to application selector.
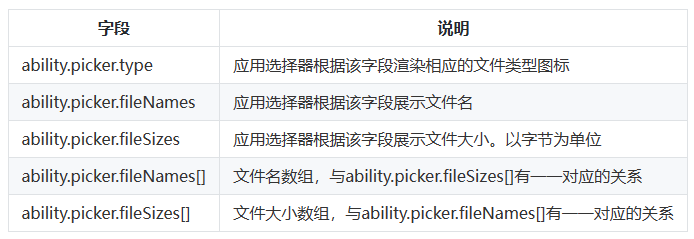
parameters: {
// The MIME type of pdf
"ability.picker.type": "application/pdf",
"ability.picker.fileNames": [path],
"ability.picker.fileSizes": [fileSize],
// This a nested want which will be directly send to the user selected application.
"ability.want.params.INTENT": {
"action": "ohos.want.action.sendData",
"type": "application/pdf",
"parameters": {
"keyFd": {"type": "FD", "value": fileFd}
}
}
}
}
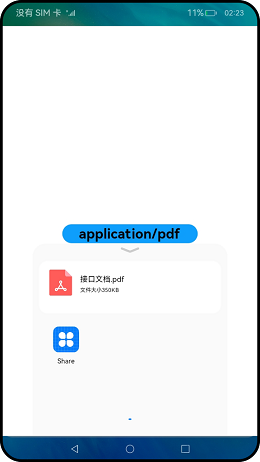
2、被分享方
定义skills
"skills": [
{
"entities": [
// ...
],
"actions": [
"ohos.want.action.sendData"
// ...
],
"uris": [
{
"type": "application/pdf"
},
// ...
]
},
]
2、接收数据
onCreate(want, launchParam) {
// note when keyFd is undefined, app crash will happen.
if (want["parameters"]["keyFd"] !== undefined) {
// receive file descriptor
let fd = want["parameters"]["keyFd"].value;
// ...
}
}
🚀写在最后
- 如果你觉得这篇内容对你还蛮有帮助,我想邀请你帮我三个小忙:
- 点赞,转发,有你们的 『点赞和评论』,才是我创造的动力。
- 关注小编,同时可以期待后续文章ing🚀,不定期分享原创知识。
- 更多鸿蒙最新技术知识点,请关注作者博客:https://t.doruo.cn/14DjR1rEY
